So what is Emasculation?
The literal meaning of emasculation is the removal of the penis and the testicles, the external male sex organs. Removal of the testicles alone is termed castration. Emasculation was a form of punishment in Medieval Europe and sometimes formed part of the process of being hanged, drawn and quartered.
By extension, the word has also come to mean to render a male less of a man, or to make a male feel less of a man by humiliation. Needless to say, this metaphorical usage of the word is much more common than the application of its literal meaning.
Masculinity
In order to better understand this metaphorical usage, it's necessary to take a look a masculinity.
Masculinity (also called boyhood, manliness, machismo, or manhood) is a set of attributes, behaviors and roles generally associated with boys and men. Masculinity is socially constructed, but made up of both socially-defined and biologically-created factors, distinct from the definition of the male biological sex.
Both males and females can exhibit masculine traits and behavior. Those exhibiting both masculine and feminine characteristics are considered androgynous, and feminist philosophers have argued that gender ambiguity may blur gender classification.
Masculine traits include courage, independence and assertiveness. These traits vary by location and context, and are influenced by social and cultural factors.
Masculine qualities, characteristics or roles are considered typical of, or appropriate for, a boy or man. They have degrees of comparison: "more masculine" and "most masculine", and the opposite may be expressed by "unmanly" or "epicene". Similar to masculinity is virility (from the Latin vir, "man").
The concept of masculinity varies historically and culturally; although the dandy was seen as a 19th-century ideal of masculinity, he is considered effeminate by modern standards. Masculine norms, as described in Ronald F. Levant's Masculinity Reconstructed, are "avoidance of femininity; restricted emotions; sex disconnected from intimacy; pursuit of achievement and status; self-reliance; strength and aggression, and homophobia." These norms reinforce gender roles by associating attributes and characteristics with one gender.
In many cultures, displaying characteristics not typical of one's gender may be a social problem. In sociology, this labeling is known as gender assumptions and is part of socialization to meet the mores of a society. Non-standard behavior may be considered indicative of homosexuality, despite the fact that gender expression, gender identity and sexual orientation are widely accepted as distinct concepts.
The relative importance of socialization and genetics in the development of masculinity is debated. Although social conditioning is believed to play a role, psychologists and psychoanalysts such as Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung believed that aspects of "feminine" and "masculine" identity are subconsciously present in all human males.
Femininity
And now let's take a look a femininity.
Femininity (also called femininity, girlishness, marianismo, womanliness or womanhood) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with girls and women. Femininity is made up of both socially-defined and biologically-created factors. This makes it distinct from the definition of the biological female sex, as both males and females can exhibit feminine traits.
Modern conceptualizations of femininity also rely not just upon social constructions, but upon the individualized choices made by women:
Traits traditionally cited as feminine include gentleness, empathy, and sensitivity, though traits associated with femininity vary depending on location and context, and are influenced by a variety of social and cultural factors.
History
Tara Williams has suggested that modern notions of femininity in English speaking society began during the English medieval period at the time of the bubonic plague in the 1300s. Women in the Early Middle Ages were referred to simply within their traditional roles of maiden, wife, or widow.
After the Black Death in England wiped out approximately half the population, traditional roles of wife and mother changed, and opportunities opened up for women in society. Prudence Allen has traced how the concept of "woman" changed during this period. The words femininity and womanhood are first recorded in Chaucer around 1380.
In 1949, French intellectual Simone de Beauvoir wrote that "no biological, psychological or economic fate determines the figure that the human female presents in society" and "one is not born, but rather becomes, a woman," just as implied above that one is not born, but rather becomes, a man.
This idea was picked up in 1959 by Canadian-American sociologist Erving Goffman and in 1990 by American philosopher Judith Butler, who theorized that gender is not fixed or inherent but is rather a socially defined set of practices and traits that have, over time, grown to become labelled as feminine or masculine. Goffman argued that women are socialized to present themselves as "precious, ornamental and fragile, uninstructed in and ill-suited for anything requiring muscular exertion" and to project "shyness, reserve and a display of frailty, fear and incompetence."
Second-wave feminists, influenced by de Beauvoir, believed that although biological differences between females and males were innate, the concepts of femininity and masculinity had been culturally constructed, with traits such as passivity and tenderness assigned to women and aggression and intelligence assigned to men.
Girls, second-wave feminists said, were then socialized with toys, games, television and school into conforming to feminine values and behaviors. In her significant 1963 book The Feminine Mystique, American feminist Betty Friedan wrote that the key to women's subjugation lay in the social construction of femininity as childlike, passive and dependent, and called for a "drastic reshaping of the cultural image of femininity."
Behavior and Personality
While the defining characteristics of femininity are not universally identical, some patterns exist: gentleness, empathy, sensitivity, caring, sweetness, compassion, tolerance, nurturance, deference, and succorance are traits that have traditionally been cited as feminine.
Femininity is sometimes linked with sexual objectification and sexual appeal. Sexual passiveness, or sexual receptivity, is sometimes considered feminine while sexual assertiveness and sexual desire is sometimes considered masculine.
An ongoing debate with regards to sex and psychology concerns the extent to which gender identity and gender-specific behavior is due to socialization versus inborn factors. According to Diane F. Halpern, both factors play a role, but the relative importance of each must still be investigated. The nature versus nurture question, for example, is extensively debated and is continually revitalized by new research findings. Some hold that feminine identity is partly a 'given' and partly a goal to be sought, just a as is the case with masculine identity.
In 1959, researchers such as John Money and Anke Erhardt proposed the prenatal hormone theory. Their research argues that sexual organs bath the embryo with hormones in the womb, resulting in the birth of an individual with a distinctively male or female brain; this was suggested by some to "predict future behavioral development in a masculine or feminine direction". This theory, however, has been criticized on theoretical and empirical grounds and remains controversial. In 2005, scientific research investigating sex and psychology showed that gender expectations and stereotype threat affect behavior, and a person's gender identity can develop as early as three years of age. Money also argued that gender identity is formed during a child's first three years.
Mary Vetterling-Braggin argues that all characteristics associated with femininity arose from early human sexual encounters which were mainly male-forced and female-unwilling, because of male and female anatomical differences. Others, such as Carole Pateman, Ria Kloppenborg, and Wouter J. Hanegraaff, argue that the definition of femininity is the result of how females must behave in order to maintain a patriarchal social system.
In his 1998 book Masculinity and Femininity: the Taboo Dimension of National Cultures, Dutch psychologist and researcher Geert Hofstede wrote that only behaviors directly connected with procreation can, strictly speaking, be described as feminine or masculine, and yet every society worldwide recognizes many additional behaviors as more suitable to females than males, and vice versa. He describes these as relatively arbitrary choices mediated by cultural norms and traditions.
Hofstede describes as feminine behaviors such as "service", "permissiveness", and "benevolence", and describes as feminine those countries stressing equality, solidarity, quality of , and the resolution of conflicts by compromise and negotiation.
Clothing and appearance
In Western cultures, the ideal of feminine appearance has traditionally included long, flowing hair, clear skin, a narrow waist, and little or no body hair or facial hair. In other cultures, however, expectations are different. For example, in many parts of the world, underarm hair is not considered unfeminine. Today, the color pink is strongly associated with femininity, whereas in the early 1900s pink was associated with boys and blue with girls.
These feminine ideals of beauty have been criticized by feminists and others as restrictive, unhealthy, and even racist. In particular, the prevalence of anorexia and other eating disorders in Western countries has frequently been blamed on the modern feminine ideal of thinness.
In many Muslim countries, women are required to cover their heads with a hijab (veil). It is considered a symbol of feminine modesty and morality.
Cultural standards vary a great deal on what is considered feminine. For example, in 16th century France, high heels were considered a distinctly masculine type of shoe, though they are currently considered feminine.
In Ancient Egypt, sheath and beaded net dresses were considered female clothing, while wraparound dresses, perfumes, cosmetics, and elaborate jewelry were worn by both men and women. In Ancient Persia, clothing was generally unisex, though women wore veils and headscarves.
Gender Identity - Nature vs. Nurture
The extent to which masculinity or femininity is inborn or conditioned is debated. How a child develops gender identity is also debated. Some believe that masculinity is linked to the male body while femininity is linked to the female body; in this view, masculinity is associated with male genitalia and femininity is associated with the female genitalia. Others have suggested that although masculinity may be influenced by biology, it is also a cultural construct.
Recent research has been done on an individual's self concept of masculinity and its relation to testosterone; the results have shown that masculinity not only differs in different cultures, but the levels of testosterone do not predict how masculine or feminine one feels.
On the nurture side of the debate, it is argued that masculinity or femininity do not have a single source. Although the military has a vested interest in constructing and promoting a specific form of masculinity, it does not create it.
Research at the Johns Hopkins Children Center has shown that gender identity is almost entirely based on nature and is almost exclusively predetermined before the birth of the baby. Two studies conducted by William Reiner, a child and adolescent psychiatrist and urologist, have confirmed that the amount of exposure to male hormones and androgens in utero almost exclusively decides whether the child identifies as masculine or feminine.
In the first study, Reiner followed 14 children whose testicles and male hormone levels were completely normal at birth, but who were born without a penis — 12 of the children were surgically reconstructed to appear female. Today, all 12 of the children raised as females are strongly male a-typical in their behaviors, attitudes, friends and play and 6 of the 12 have already reassumed their male gender identities at the ages of 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, and 12 respectively. The 2 children who did not undergo sex reassignment surgeries as infants developed far more normally and more similarly to their normal male peers and were much more psychologically well adjusted than the sex-reassigned children.
In the second study, Reiner followed 12 genetically male children who were born with a similar defect, in that they lacked a penis at birth. All of these children underwent a sex reassignment surgery to appear female in infancy. Since then, 8 of the 12 have reassigned themselves back to a male identity. Of the the 4 who remain female, 3 of the sets of parents plan to tell their child about their genetic sex at birth “soon” and all 3 sets of parents expect that their children will switch back to a masculine identity after learning about their birth sex.
Reiner comments on the results of the studies stating, “These studies suggest that male gender identity is directly related to normal male patterns of male hormone exposure in utero. These children demonstrate that normal male gender identity can develop not only in the absence of the penis, but even after the removal of testicles or castration at birth, and unequivocal rearing as female. Rather than the environment forming these children’s gender identity, their identity and gender role seem to have developed despite a total environment telling them they were female.” These and consequent other studies have caused the scientific community to reevaluate their belief that gender identity is constructed through “nurture”.
Most scientists now believe that gender identity is something that is predetermined by a biological aspect and cannot be chosen for a child.
This new outlook has called for the reevaluation of sex reassignment surgeries on infants and parents who are considering one for their child are urged with extreme caution to consider letting their child decide on their own at a later age. Reiner believes, “These studies indicate that with time and age, children may well know what their gender is, regardless of any and all information and child-rearing to the contrary. They seem to be quite capable of telling us who they are.”
Male and Female Genetic Differences
Humans are genderless at the point of conception but are all genetically female at conception. (Ryder and Sigelman, 2010) In order for a blastocysts or embryo to be genetically male a Y chromosome must be introduced in the correct sequence and location. At this stage, this is the only separation between the two. The Y chromosome contains hundreds of thousands of genes completed different from those contained in the X chromosome. These X and Y genes have been identified as a rather strong predictor of differences between the identities of men and women as they influence not just appearance but human behaviors and to a large extent human intelligence.
Examining the genetic argument from a reductionist view, evidence suggests that chromosomal orientation is in fact crucial to the sexual development of humans. Humans are born with 23 pairs of chromosomes. As mentioned above the X and Y chromosomes determine a person’s sex.
The most common genotype for the ‘normal female’ and the ‘normal male’ is 46XX and 46XY respectively.
It would be simple to only have these two results however this is not the case. A few births per thousand some individuals are born with a single sex chromosome 45X or 45Y or some with three or more sex chromosomes.
Prenatal Considerations
There is an increasing amount of research information showing that the prenatal environment is critical to the presentation of gender identity. The dominating factor in this environment is the balance of hormones that the developing fetus is subjected to.
Genetic information determines whether the primordial gonads, which are originally identical in males and females, develop as testes or ovaries. This is called sex determination. Once the gonads have developed as testes or ovaries, their hormonal products, particularly testicular hormones, determine physical development as male or female, a process called sexual differentiation. In human beings, the testes become active at about week 7 to 8 of gestation. Testicular hormones cause the external genitalia to develop in the male pattern (penis and scrotum), and in the absence of testicular hormones, the external genitalia develop in the female pattern (clitoris and labia). As outlined below, similar processes of sexual differentiation under the control of gonadal steroids occur in the mammalian brain during early development.
Testosterone and estrogen are present in both males and females, with the principal active estrogen in both sexes being Estrodial (E2). The active portion of circulating E2 and of testosterone (T), is the free hormone, which is not bound to its specific plasma binding TBEG (testosterone-estrogen binding globulin or sex hormone binding globulin).
The concentration of TBEG is sex hormone dependent, undergoing activation under estrogenic stimulation and suppression as a result of androgens. There is a dynamic antagonism between androgens and estrogens such that the biological effects of one may be inhibited by the presence of the other. Although the biochemical basis of this inhibition is unknown, its influence in disease states associated with devirilizing or feminizing changes is clear.
Gonadal steroids have two general types of influences on brain and behavior, and they have been called organizational effects or influences and activational effects or influences. Organizational and activational effects are distinguished by their timing and their permanence. Organizational influences typically occur early in life, particularly prenatally and neonatally, and they are enduring. In contrast, activational influences occur later in life, typically in adulthood, and they are transient, waxing and waning as hormone levels rise or fall. An example is the activation of female sexual behavior by estrogen and progesterone near the time of ovulation, and the decline in sexual behavior at other phases of the cycle, when these hormones decline.
Androgens, produced by the testes in males and the adrenal cortex in both sexes, appear to have a profound organizational effect on early neural development. Female rats exposed neonatally to androgens will mount other rats, which is a typical male mating behavior. Likewise, male rats deprived of androgen from an early age will exhibit lordosis, which is a typical female mating behavior of adopting the naturally occurring position for sexual receptivity. Males can be deprived of androgens by castration or prenatal exposure to alcohol or stress, which lower prenatal surges of testosterone in male fetuses. Castrated males are much less likely to behave sexually because of a lack of testosterone, a principle androgen. Administration of testosterone will increase the level of sexual activity exhibited by a castrated male. Castrated males also display an increase in lordosis.
Several general principles of organizational influences are worth noting. One is that they typically occur during critical, or sensitive, periods of development, and these periods occur at times when testosterone is elevated in developing male animals. One implication of this general principle is that the hormone must be present at the appropriate time to have its effect. If it is present too early or too late, the impact will not be the same. In addition, although present only briefly, the impact of exposure to the hormone at the appropriate time can persist across the lifespan.
It is hard to get information on hormone levels in developing humans. However, the small amount of available information examining testosterone levels in human fetuses and neonates suggests that there is a marked elevation in testosterone in males compared to females beginning by about week 8 of gestation and tapering off by week 24, and again shortly after birth, from about the first to the third month of infancy.
Regardless of the timing of this sex difference, testosterone appears to be higher very early in infancy in boys than in girls. The gonads are relatively quiescent following this early testosterone elevation in boys, until of course, the dramatic sex differences in testosterone and other gonadal steroids that begin at puberty.
According to the classical model of hormonal influences on mammalian sexual differentiation, prenatal or neonatal exposure to testicular hormones causes male-typical development, whereas female-typical development occurs in the absence of testicular hormones. A corollary of this formulation is that ovarian steroids are not required for female-typical development.
The empirical record generally supports this model for a wide range of brain regions and behaviors that differ on the average for male and female animals. For example, treating female rodents with testosterone early in life decreases their female-typical behavior in adulthood, and increases their male-typical behavior. Similarly, castrating male rodents early in life leads to decreased male-typical, and increased female-typical, behavior subsequently. The same manipulations produce neural changes as well. Early testosterone treatment of female rats increases the volume of sexually-dimorphic nucleus of the preoptic area (SDN-POA), a region of the anterior hypothalamic preoptic area that is larger in male than in female rats, and castration of male rats early in life reduces the volume of the same nucleus.
In contrast to the effects on male animals of removing the testes early in life, removal of the ovaries at this time does not have substantial effects on sexual differentiation of female animals. It does not, for instance, reduce their ability to show female-typical sexual behavior in adulthood, assuming appropriate activating hormones are replaced at that time.
Although male and female sexual behaviors have been studied more thoroughly than other sex-related behaviors, it is likely that each aspect of behavior that is influenced by the early hormone environment is regulated by somewhat different neural circuitry and involves somewhat different specific mechanisms. These different specific mechanisms could include, for example, different times of maximal sensitivity, sensitivity to different metabolites of testosterone and involvement of different downstream processes.
A feminized male in feminine office wear.
Nevertheless, studies where hormones have been manipulated experimentally in a wide variety of mammalian species, ranging from rodents to rhesus monkeys, indicate that exposure to high levels of testosterone during critical periods of early development promotes male-typical neural and behavioral development, whereas exposure to lower levels of testosterone leads to female-typical neural and behavioral development. Given the large sex difference in human sexual orientation, the hypothesis that the early hormone environment influences this sexually differentiated outcome merits [increasing] investigation.
Testosterone and estrogen are no longer considered male only and female only hormones. Both hormones are important in both sexes. It was known as early as the 1930's that developmental exposure to a high dose of estrogen causes malformation of the male reproductive tract, but the early formative years of reproductive biology as a discipline did not recognize the importance of estrogen in regulating the normal function of the adult male reproductive tract.
In the adult testis, estrogen is synthesized by Leydig cells and the germ cells, producing a relatively high concentration in rete testis fluid. Estrogen receptors are present in the testis, efferent ductules and epididymis of most species. However, estrogen receptor-α is reported absent in the testis of a few species, including man. Estrogen receptors are abundant in the efferent ductule epithelium, where their primary function is to regulate the expression of proteins involved in fluid reabsorption.
Estrogen's primary function in the male tract appears to be the regulation of fluid reabsorption in the efferent ductules. Disruption of the receptor results in eventual decreased fertility.
Testosterone can be converted to estradiol, an estrogen, by aromatase, an enzyme. The conversion of testosterone is essential to the masculinization of the male rat brain, and possibly the brains of other mammals. Male rats deprived of aromatase develop female-like patterns of learning. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a blood protein, protects female rat pups from the masculinizing effects of estrogen. AFP binds to estrogen and ensures that estrogen will not be absorbed by neurons as easily. Synthetic estrogen, which does not bind to AFP, and high doses of estradiol can cause females to exhibit masculine mating behaviors, indicating that biosynthesized estradiol is essential in the process of neural masculinization.
Placement of estradiol in the hippocampus or cortex of neonatally castrated males reinstates a learning behavior typical of males that is generally absent in castrated males, further indicating that estradiol is an important chemical in the masculinization process. The sexually dimorphic nucleus of the preoptic area (SDN-POA) is eight times larger in male rats than female rats. A female rat treated with testosterone or synthetic estrogen will have a larger SDN-POA. Estrogen appears to enlarge the SDN-POA by preventing cell death in the area.
Curiously, estrogen causes masculinization in males and feminization in females. This is possible because of several differences between males and females. First, the level of estrogen is much higher in males because high levels of testosterone can be aromatized, compared with the relatively low level of estrogen in prepubescent rats. Second, males and females have critical periods of estrogen sensitivity. Male rats are sensitive to estrogen relatively early in development, while female rats are sensitive later and for a longer period of time. Finally, male and female rats have different receptor populations that are influenced by age. These factors ensure different patterns of growth and development in males and females.
Behavioral differences between the sexes indicate that males and females differ in the structure and function of their nervous systems. Research supports this postulation. Yet, researching biological differences between the sexes is discouraged by some people who fear that women will be found biologically inferior, and that dangerous or hurtful behaviors such as "aggression, rape, and philandering" will be found to be innate, and therefore incurable. However, limiting our understanding of the male and female nervous systems is not helpful. Understanding the nervous system aids in understanding behavior. Biology may explain behavior, but it does not justify it. If the origin of a harmful behavior is understood, a method of preventing the behavior can be found. The neurological differences between the sexes are considerably variable, including differences in patterns of mylination, and hippocampal and cortical morphology.
Defeminization and Masculinization
Defeminization and masculinization are the processes that a fetus goes through to become a male.
It has often been said by biologists that in sexual differentiation in mammals, the female is the "default" developmental pathway, in the sense that elimination of any of several gene actions necessary for formation of male genitalia leads to the development of external female genitalia (though development of functional ovaries requires effective action of several less understood sex-specific genes). Two processes: defeminization, and masculinization, are involved in producing male typical morphology and behavior. Disruption of either of these processes in males produces female-typical development. The opposite is not true, in that the disruption of normal sexual development in females does not lead to male-typical endpoints.
Defeminization involves the suppression of the development of female typical morphology (development of the Müllerian ducts into the fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina) and behavioural predispositions. Masculinization involves the production of male typical morphology (development of the Wolffian ducts into male reproductive structures) and behavioral predispositions. Both defeminization and masculinization are required for a mammalian zygote to become a fully reproductively functional male.
A brief version of the female default paradigm can be stated as follows:
A set of specific genetic instructions must be present and a series of differentiating events mediated by hormones must occur in order for a mammalian zygote to become a fully reproductively functional male.
The SRY, SOX9, and SF1 genes must be present and functional.
Functional Leydig cells must form in the gonads.
The Leydig cells must be able to produce testosterone.
The target cells must have the hormone receptors to respond to the testosterone. The target cells of the external genitalia must have functional 5-alpha-reductase enzyme to convert some of the testosterone to more active dihydrotestosterone.
There is some evidence that the brain must be exposed and respond to androgens either prenatally or early in life to produce characteristic mating behavior. This is well demonstrated in many animal species.
To a large extent, each step builds on the previous. If anything goes wrong at any of the first four steps, the subsequent pathway of development results in female anatomy and behavior.
No ovarian organizing gene homologous to SRY has been discovered. Both sexes are exposed to maternal estrogen prenatally. No hormones have yet been discovered that are necessary early in life to produce female sexual development. Estrogen seems not to be necessary until puberty for purposes of differentiation.
a. The full development of male characteristics also includes personal experience throughout life, determining gender identity, gender roles and sexual orientation. However, there is much debate on the balance between nature and nurture in the determination.
Definition and assessment of sexual orientation in humans
Sexual Definition and assessment of sexual orientation in humans typically is conceptualized as the direction of erotic interest – in males (androphilic), in females (gynephilic), or in both. In addition to these three categories, some individuals do not report erotic interest in either sex.
It also is important to distinguish sexual orientation from other aspects of sexual identity, including core gender identity, and gender role behaviors. Core gender identity is the sense of self, usually as male or female, but occasionally as intersex or neither. Gender role behaviors are those behaviors that are culturally associated with one sex or the other. They also can be defined empirically as behaviors that show sex differences, meaning that they differ on the average for males and females in a given cultural group. These three categories of behavior might be expected to be consistent, but this is not always the case.
Although many men understand themselves to be male, are interested in female sexual partners, and engage in male-typical behaviors in other areas, such as watching or playing football, this is not always so. The situation is similar for women, as well as for girls and boys. Behavior across these three categories, or across the many types of behavior included in the concept of gender role behavior, is not always consistent for a given individual. Nevertheless, there is some consistency, and the hormonal factors that influence sexual orientation also influence other aspects of sex-typed behavior, including childhood toy, playmate and activity preferences and assessment of sexual orientation in humans.
Do hormones have activational influences on sexual orientation in adulthood?
There are no apparent hormonal differences in adulthood between men who are heterosexual and those who are not. Similarly, no such differences have been reported consistently in heterosexual compared to non-heterosexual women, although there may be a slight elevation of androgens in some homosexual women. Consistent with these findings, men who become hypogonadal in adulthood do not change their sexual orientation, though their sexual interest declines. Similarly, although men and women sometimes are treated with androgen or estrogen for medical reasons, this does not appear to alter their sexual orientation.
Definition and assessment of sexual orientation in humans
Ladyboys in Thailand
Although both virilization of the external genitalia and neurobehavioral virilization depend on testosterone and its metabolites, there are many ways in which they can be decoupled. For instance, the time period when androgen influences development of the external genitalia is earlier in gestation than the time when most neurobehavioral effects are seen. Also, different co-factors are involved in masculinization of different neural regions, and similar differences in the co-factors whose action is required are likely to exist for the genitalia versus whatever neural systems are involved in hormonal influences on sexual orientation. Similarly, testosterone acts on the external genitalia largely following conversion to DHT, but may require conversion to estradiol before exerting some of its neurobehavioral effects.
If more of the testosterone these men produce is converted to DHT in the periphery, less could be available for conversion to estradiol in the brain, thus leading to greater masculinization of the external genitalia, but reduced neurobehavioral masculinization.
Prenatal stress and sexual orientation
Stress alters production of adrenal hormones, including testosterone and other androgens, raising the question of whether prenatal stress could influence sexual orientation. In rats, stressing pregnant animals increases female-typical sexual behavior in male offspring. These effects resemble those seen following reduction of androgen in developing male animals, for example by castration, and the effect of stress on development of male rats has been suggested to occur because it disrupts a prenatal surge of testosterone that occurs in typically-developing males.
Possible reconciliations of the findings for humans versus rodents involve differences in the adrenal response to stress, and differences in the length of pregnancy. The adrenal response to stress appears to be less dramatic in humans than in rodents. In addition, human gestation and the period of prenatal sexual differentiation is far longer in humans than in rats, appearing to last for approximately 2 days in rats, but for months in humans. This additional time may allow feedback mechanisms in the human male fetus to adjust testicular androgen production to compensate for alterations in stress-related adrenal androgen secretion.
As with so many other physiological aspects of homeostasis, feedback mechanisms can ameliorate some of the common stress related disruptions to androgen secretion, which, for most gestating males, leads to normal sexual development.
Sexual orientation and childhood behavior
A female vervet monkey conducting an anogenital inspection (examining the genital area of the doll in an attempt to determine whether it is male or female), and a male vervet monkey pushing a police car back and forth.
Boys and girls differ, on average, in their toy, playmate and activity preferences. Boys tend to prefer toys like vehicles, such as cars, trains, trucks and airplanes, and weapons, whereas girls tend to prefer toys like dolls and tea sets. Sex differences in toy preferences appear in infancy, at least by the age of 12 months, and they grow larger as children develop into middle childhood. The mode of assessment (e.g., questionnaire versus observation) and the specific toys involved can influence the size of the sex differences, but behavioral observation of toy choices in childhood can show large sex differences for both masculine and feminine toys.
A new study by researchers at the City University of London found that babies as young as 9 months old prefer to play with toys specific to their own gender.
The experimenters, whose results were published in the journal Infant and Child Development this month, put 101 girls and boys between the ages of 9 and 32 months in a nursery with a variety of toys and observed which ones the children seemed to play with more.
The toys used in the study were a doll, a pink teddy bear, a cooking pot, a car, a blue teddy, a digger and a ball. Toys were placed a few feet from the children so they would have to make some effort to get to them, and then researchers observed not only which ones they chose, but also how they played with them and for how long.
Among the youngest, they found, the boys tended to prefer the ball and the girls wanted the pot.
While modern parents like to think that everything is in our control when it comes to socializing children, the researchers found the opposite to be true. They write: “Our findings of sex differences in toy choice in the 9 to 17 months age group add some weight to the suggestion that such preferences appear prior to extensive socialization and do not depend on gender category knowledge but are reflections of our biological heritage.
So is our gender divide in toys entirely the product of nature? Obviously not.
In fact, the researchers observed that babies and toddlers made almost no distinction between the blue and the pink teddy bears they were offered. Which suggests that certain things, like the color of a toy, only matter once kids are socialized to certain ideas — namely that pink is for girls and blue is for boys.
In regard to playmate preferences, 80-90% of children’s play partners are typically of their own sex. This sex difference also grows larger as children grow older; children at age 4.5 years spend about three times as much time with peers of their own than the other sex, whereas at age 6.5 years, they spend 10 times as much time with same sexed as with other sexed peers. In regard to activities, boys, like other male mammals, tend to engage in more rough and tumble play, involving overall body contact and playful aggression, than do girls. This sex difference is large for children playing with other children of the same sex.
An individual’s sexual orientation typically becomes apparent after puberty. However, there is evidence that most men who are not heterosexual recall having been sex-atypical in their childhood behavior, particularly in their sex-typed toy, playmate and activity interests.
Hormones and sexual differentiation of childhood behavior
There is substantial evidence that exposure to androgens prenatally influences children’s sex-typical toy, activity and playmate preferences. A consistent research finding, for example, is that girls who were exposed to high levels of testosterone prenatally, show increased male-typical toy preferences, playmate preferences and activity interests.
These effects have been seen in studies conducted in a number of different countries in North America and Europe and using various methodologies, including interviews, questionnaires and direct observation of behavior. The results of these studies are consistent with the hypothesis that prenatal exposure to androgens influences the development of children’s sex-typical toy, activity and playmate preferences. Evidence from situations where women were prescribed hormones during pregnancy for medical reasons also support a role for androgens prenatally in the development of children’s sex typed interests. Children whose mothers took androgenic progestins during pregnancy show increased male-typical or decreased female-typical behavior, and those whose mothers took anti-androgenic progestins show the opposite outcome.
Girls whose mothers took androgenic progestins while pregnant, typically are born with virilized genitalia, leading to suggestions that physical virilization could cause increased male-typical behavior. These suggestions have been addressed by showing that normal variability in androgen exposure prenatally is associated with normal variability in sex-typed toy, activity and playmate preferences postnatally.
Pathways to sexual orientation
The factors leading to individual variability in most human psychological and behavioral characteristics are rarely singular. In most cases, several types of factors combine to produce a particular outcome. In addition, a number of different pathways can lead to a common outcome. Sexual orientation outcomes are likely to be similarly determined by multiple factors, and to have more than one multi-factored pathway leading to an outcome, such as androphilic orientation, gynephilic orientation or bisexual orientation.
This article addressed the question of whether gonadal steroid exposure during prenatal development is one of the factors, in at least one of the pathways, that lead to variability in sexual orientation outcomes. Based on the compelling evidence that prenatal testosterone exposure influences children’s sex-typical play behavior, on the well-established links between childhood play interests and adult sexual orientation, and on the evidence showing altered sexual orientation in women exposed to high levels of androgens prenatally, the answer appears to be “yes”.
It is worth discussing the reason for the link between sex-atypical toy, playmate and activity interests in childhood and sex-atypical sexual orientation in adulthood. A highly likely explanation is that the prenatal hormone environment influences both of these sex-related characteristics, childhood toy, playmate and activity interests and sexual orientation, directly, by acting during early development on the neural systems that regulate them.
Hormonal Production Pathways and Emasculation
At the beginning of the pathway Cholesterol is made from low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
Cholesterol is converted to pregnenolone with the assistance of Vitamin A and free T3 (triiodothyronine).
Pregnenolone is the precursor to many other hormones.
Pregnenolone gets converted to 17 hydroxy pregnenolone or to Progesterone.
17 hydroxy pregnenolone gets converted to DHEA.
DHEA can be converted to Androstenedione.
Androstendione can be converted to testosterone.
Testosterone is finally converted to dihydrotestosterone.
Progesterone gets converted to 17 hydroxyprogesterone or Corticosterone.
17 hydroxyprogesterone converts to 11 deoxycortisol.
11 deoxycortisol converts finally to cortisol.
Corticosterone converts to aldosterone which plays a role in fluid electrolyte balance.
Back to Androstendione which can also be converted to Estrone (E1).
Estrone can convert back and forth with itself and estradiol(E2).
E1 or E2 can covert to Estriol (E3), but this step is irreversible
Since cholesterol is the critical substance that the other steroid hormones are derived from, a low-cholesterol prenatal diet can lead to a reduction of the ideal hormone levels necessary for optimal sexual development in the fetus.
To make steroids we need an adequate amount of thyroid hormone (T3) and vitamin A around to convert the cholesterol to pregnenolone and then to DHEA. So if someone is hypothyroid and/or has low vitamin A levels they will be unable to produce optimal levels of pregnenolone and DHEA.
This means that all the steroids formed from cholesterol will also be lower if this continues chronically. That means the sex steroid hormones also fall, and so does Vitamin D levels.
The other affect of hypothyroidism is that it causes decreased steroid synthesis due to pregnenolone steal syndrome. Steroids secretion is how the brain maintains control over the twenty trillion cells in our bodies. If you can’t make the chemicals the brain needs to maintain this control, all hell can break loose from a control stand point.
Anytime cellular stress is high, it also forces all the hormone backbone substrate called pregnenolone to be shunted to cortisol production. This is called pregnenolone steal syndrome. What exactly does this mean? DHEA, Androstenedione, Vitamin D, testosterone, estrogen, and aldosterone production all fall dramatically. These are all of the hormones that are made from a common precursor. What type of stressors lead to pregnenolone steal? ANY form of stress: blood sugar imbalances, circadian disruption, emotional stress, malabsorption, systemic infections, dental infections, dysbiosis and many others.
It's also important to keep in mind that high cortisol directly blocks 5′ deiodinase enzyme that converts T4 to T3. Cortisol Releasing Hormone (CRH) (seen elevated in high cortisol production states) directly blocks thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The implication is huge because Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and T3, the active thyroid hormone, are inhibited quickly in this process. Immediately, any excess T4 is then shunted to reverse T3. Reverse T3 is a competitive inhibitor to T3, the active thyroid hormone. This basically turns off the thyroid, which further reduces the production of sex steroids.
The net effect here is that high stress levels during the prenatal development, can have a dramatic effect on the optimal production of steroid hormones, with the resulting reduced levels of testosterone impacting the normal sexual development of the male fetus. The effect of this reduction will obviously be much stronger if the decrease occurs at critical stages of that sexual development.
When cholesterol production is also inadequate and nutritional deficiencies exist for vitamin A, Iodine, along with other key substances for steroid conversion, the potential for suboptimal sexual development increases dramatically.
And since testicular hormones cause the external genitalia to develop in the male pattern (penis and scrotum), and in the absence of testicular hormones, the external genitalia develop in the female pattern (clitoris and labia), low levels of these hormones can have varying effects on the sexual development of the male.
Testicular hormone levels have been shown to affect a wide range of brain regions and behaviors that differ on the average for male and female animals. Treating female rodents with testosterone early in life decreases their female-typical behavior in adulthood, and increases their male-typical behavior. Similarly, castrating male rodents early in life leads to decreased male-typical, and increased female-typical, behavior subsequently. The same manipulations produce neural changes as well.
Myelin Sheath Connection
Research has also shown that female brain development produces a decreased thickness of the myelin sheathing. Myelin is a biologic dielectric material that forms a layer, the myelin sheath, usually around only the axon of a neuron. Dielectrics are electrical insulating materials found in nature.
Myelin is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system, specifically the formation of the nerve action potential. Myelin decreases capacitance across the cell membrane, and increases electrical resistance. Thus, myelination helps prevent the electrical current from leaving the axon. It also protects the neuron from electromagnetic fields because of this ability.
The decreased thickness of the brain's myelin sheathing increases the sensitivity to an external stimulus, which is thought to be particularly necessary in the female to insure the successful gestation and rearing of young humans, increasing the awareness and avoidance of potential lethal dangers.
The reduction of optimal levels of testicular steroids may contribute to this reduced thickness of the myelin sheath, increasing the environmental sensitivity that is evident with the female brain.
Infants, who have had minimal exposure to social conventions, do display variation between male and female behavior. Human female infants tend to be more sensitive to touch than male infants are. One study reported that the least sensitive female infant in a sample may be more sensitive than the most sensitive male infant. Female infants are often more sensitive to sound and are more easily agitated by noise than male infants. Baby girls seem to be more social, as well. They are more inclined to "gurgle" at people and to recognize familiar faces than baby boys. The behavioral differences between infants of different sexes appear very early in life, indicating that the mechanism controlling these behavioral patterns is innate and not learned from society.
Chemical Emasculation and Feminization
An increasing amount of research information is showing that the ingestion, absorption or inhalation of synthetic particular chemical substances drastically impacts the hormonal balance of male physiology and female physiology as well.
To the extent that these substances create an imbalance in the pregnant woman or cross the placental barrier into the fetus, they will also have negative effects on the hormonal balance and sexual development of the male or female. Once the child is born, the exposure to these substances will continue to impact the sexual development until maturity is reached.
Most of the research information has focused on the activational effects that occur from these chemical substances. As stated above, activational influences occur later in life, typically in adulthood, and they are transient, waxing and waning as hormone levels rise or fall.
According to a recent study, "Falling sperm counts could be caused by traces of the contraceptive pill in drinking water."
U.S. scientists say the sex hormone oestradiol - the birth control hormone that passes untreated through sewage plants - has an even larger effect on sperm than Bisphenol A or BPA, as it is widely known. BPA is found in some plastics used to make food containers, bottles" and coatings in tin cans, and is also commonly used in thermal paper in cash register receipts.
Make no mistake, BPA isn't the only method being utilized, there are also a whole host of xenoestrogens found in everything from suntan lotions to the food we eat, all " clinically significant because they can mimic the effects of endogenous estrogen and thus have been implicated in precocious puberty and other disorders of the reproductive system.
Via the Women In Balance Institute, we see a partial list of things used every day in America which include the chemicals that are xenoestrogens, including:
• Industrial products and Plastics: • Bisphenol A (monomer for polycarbonate plastic and epoxy resin; antioxidant in plasticizers); • Phthalates (plasticizers); • DEHP (plasticizer for PVC); • Polybrominated biphenyl ethers (PBDEs) (flame retardants used in plastics, foams, building materials, electronics, furnishings, motor vehicles); • Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs);
• Food:• Erythrosine / FD&C Red No. 3; • Phenosulfothiazine (a red dye)• Butylated hydroxyanisole / BHA (food preservative); • Building supplies: • Pentachlorophenol (general biocide and wood preservative); • Polychlorinated biphenyls / PCBs (in electrical oils, lubricants, adhesives, paints);
• Insecticides: • Atrazine (weed killer); • DDT (insecticide, banned); • Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (one of the breakdown products of DDT); • Dieldrin (insecticide); • Endosulfan (insecticide); • Heptachlor (insecticide); • Lindane / hexachlorocyclohexane (insecticide, used to treat lice and scabies); • Methoxychlor (insecticide); • Fenthion; • Nonylphenol and derivatives (industrial surfactants; emulsifiers for emulsion polymerization; laboratory detergents; pesticides);
• Other: • Propyl gallate; • Chlorine and chlorine by-products; • Ethinylestradiol (combined oral contraceptive pill); • Metalloestrogens (a class of inorganic xenoestrogens); • Alkylphenol (surfactant used in cleaning detergents; • 4-Methylbenzylidene camphor (4-MBC) (sunscreen lotions); • Parabens (methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben and butylparaben commonly used as a preservative); •Benzophenone (sunscreen lotions);
Xenoestrogens, however, come from over 70,000 different chemicals that have a known affect on our hormonal systems. DDT is a big culprit as are numerous fertilizers, herbicides and fungicides used by the non-organic farmers of the world. GMO crops are a huge problem, because they require larger and more pervasive use of these pesticides. Corn, soy, sugar beets, cottonseed oil, zucchini, alfalfa, and Hawaiian papaya are all predominantly grown using genetically modified seed.
We also see an amazing amount of American men going bald and with no facial hair, and/or androgynous in appearance, reminiscent of the image above from the 1971 George Lucas film THX 1138, which further addresses the point of the feminization of the American male in comparison to imported immigrants."
Elevated levels of two plastic-softening chemicals in pregnant women's urine are linked to less-masculine play behavior by their sons several years later, according to a study published in the International Journal of Andrology. Phthalates, which are used in everything from vinyl floors to plastic tubing and soaps and lotions, are pervasive in the environment and have increasingly become associated with changes in development of the male brain as well as with genital defects, metabolic abnormalities and reduced testosterone in babies and adults.
Phthalates are one of several groups of chemicals that have the power to disrupt the endocrine system, both in animals and humans. Nicknamed “gender-benders,” these chemicals are causing the males in many species to become feminized.
According to a report issued by ChemTrust last year, HALF of all male fish in British lowland rivers have been found to grow eggs in their testes! And that’s just one eye-opening example of the impact these gender bender chemicals are having on our environment.
Their study lists the symptoms found in each of the numerous species tested, which includes testicular cancer, hermaphrodites, genital deformations, low sperm counts, and infertility.
Numerous other studies over the past eight years confirm that similar dangers are posed to human health, and males are particularly at risk.
Decreased sperm motility and concentration, as well as genital abnormalities in baby boys have been linked to these chemicals.
The fact that endocrine disruptors like phthalates affect the reproductive system in nearly all mammals is becoming rather well known, although governments and public health- and safety organizations are slow to respond.
The more a pregnant woman is exposed to high levels of phthalates, the greater the risk her son will have smaller genitals and incomplete testicular descent, leading to impaired reproductive development. The chemical also appears to make the overall genital tracts of boys slightly more feminine.
It is believed that phthalates have these adverse effects because they reduce testosterone synthesis by interfering with an enzyme needed to produce the male hormone.
This latest study adds to the growing body of evidence showing the harmful effects these chemicals have on males in particular.
Women who had higher concentrations of two types of phthalates (DEHP, and DBP) also had boys who appeared more feminized in their personality, while playing.
The presence of phthalates in the mothers was not associated with any differences in the girls’ play behavior. However, that is NOT an indication that phthalates are “safe” for women.
They also affect women’s endocrine systems and reproductive health although the effects are different between the genders.
Bovine growth hormones used in food production, soy foods, and bisphenol-A (BPA), just to name a few, add to the problem as they also mimic estrogen and disrupt your endocrine system.
Other studies have linked the chemical to thyroid problems in both women and men, and researchers have also suggested a link between phthalates and illnesses like allergies, asthma, and contact dermatitis, all of which are on the rise in children.
Common Sources of Phthalates
Phthalates are found in, among other things:
Processed food packaging
Hoses
Raincoats
Shower curtains
Vinyl flooring and wall coverings
Lubricant and adhesives
Detergents
Beauty products like nail polish, hair spray, shampoo, deodorants, and fragrances
Toys
Other Gender-Bender Chemicals to Watch Out For
Endocrine disrupting chemicals are everywhere these days and can be difficult to avoid unless you take decisive steps to limit or eliminate them from your immediate surroundings. This is particularly important if you are pregnant, or planning a pregnancy.
Reading labels is a necessity these days. PVC plastics, which contain phthalates, will oftentimes carry the plastic recycling symbol # 3.
Some of the other gender-bender agents to look out for include:
Bisphenol A (BPA) -- a common ingredient in many plastics, including those in reusable water bottles and resins lining some food cans and dental sealants, can change the course of fetal development in a way that increases your risk of breast cancer.
Plastic items carrying recycling symbol # 7 is oftentimes indicative of a BPA-containing plastic.
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) -- found in grease- and water-resistant coatings like Teflon and Gore-Tex, is a likely carcinogen.
Methoxychlor and Vinclozin-- An insecticide and a fungicide respectively, have been found to cause changes to male mice born for as many as four subsequent generations after the initial exposure.
Nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEs) -- Known to be potent endocrine disrupters, these chemicals affect gene expression by turning on or off certain genes, and interfere with the way your glandular system works. They mimic the female hormone estrogen, and have been implicated as one reason behind some marine species switching from male to female.
Bovine growth hormones commonly added to commercial dairy have been implicated as a contributor to premature adolescence.
Soy products, which are loaded with hormone-like substances.
MSG -- A food additive that’s been linked to reduced fertility.
Fluoride -- This chemical in the U.S. water supply has been linked to lower fertility rates, hormone disruption and low sperm counts."(8)
Along with the overall health destroying effects of these chemicals is the feminization of males that has become so prevalent at the current time, although these effects have been building over the last 80 years, as more and more anti-testosterone disrupting chemicals have been introduced into the environment, the food supply and various products.
These chemicals act to feminize men from the time they are conceived, since the average woman's body contains close to 250 chemicals from cosmetics, household exposures, pesticides and from environmental pollution.
All of these chemicals end up in women's bodies since they're stored in fat and women have more fat tissue than men in their breasts and their hips as well as their butt. When a woman becomes pregnant she begins to expose the male fetus to these chemicals.
This happens through no fault of the woman, but through the oil, chemical and pharmaceutical companies, which produce and distribute these harmful chemicals throughout the world. Big Pharma has no incentive to reduce this exposure since they make huge profits on the 'health care' side of this situation by selling testosterone and Viagra to the millions of men who are emasculated.
By producing and distributing BPA and atrazine, which are found in a variety of foods and products which are used by the public, and which find their way into our drinking water, the chemical companies can make millions of dollars of emasculating men and lowering their testosterone levels in order to make them impotent.
As a result of this onslaught, sperm counts have decreased by 50%, while 85% of sperm cells are defective. Along with this, studies show that almost 30 million men are impotent in the US.
The majority of this damage is done in the womb. Most of these chemicals destroy the cells within the testes that produce testosterone, called the Sertroli cells. So when males are exposed to these chemicals in the womb, they don't end up with as many Sertroli cells as a normal fetus has, so their testosterone levels go down and they're less able to produce sperm.
So men today have less sperm produced than their grandfathers did and their testosterone levels are the lowest they've ever been in the history of mankind.
This damage is done in the womb and there is no way to reverse this process of feminizing men, causing them to have undescended testicles, which is a major cause of infertility, often causing them to have hyospadias, with the urethra not at the usual location at the head of the penis and often causing the penis to be no longer than 2 inches, which can lead to a tendency to change their gender identity.
This is a result of the fact that the sexual orientation and gender identity are formed in the womb and it's not a choice that's made to be bisexual, homosexual or heterosexual.
What these chemicals do is block testosterone and since all human beings are first females and have the brain of females, when testosterone is blocked, the man becomes a male and looks like a male, with male genitals, but the result is that he has the brain of a female, because the testosterone never masculanized and caused the masculazation of the brain.
So the net result is that the male animal behaves like a female, since they have the brain of a female and these chemicals can cause homosexuality.
Since these effects take place in the womb, they can end up multi-generational through epigenetic processes, which results from the chemicals changing the DNA."(9)
The effects of these chemicals on the brain also can lead to violent tendencies, while at the same time resulting in low motivation, lacking the inspiration to do anything, since testosterone levels are directly related to motivation.
These chemicals also cause adult men to look like pregnant women, with breasts and protruding bellies, since when testosterone is blocked and increase estrogen men develop belly fat which contributes to metabolic syndrome and in many cases type 2 diabetes.
This emasculation and feminization of males is all by design, since there is less need for men now that robots are taking over more and more manufacturing activities that were originally dominated by men. There's less and less need for human labor, leading to the ability of an androgenous work force to perform the remaining industrial functions.
So the oligarchs have decided that the human population will be reduced with the emasculation and feminization of men being a critical part of the process, since it leads to sterility and a drastic decrease in the procreative instinct in humans.
The following video, The Disappearing Male, gives a good overview of the extent of the problem:
The Disappearing Male! - A 2008 'Science' Documentary!
Cultural and Social Feminization
It's clear from the above information that chemical feminization of men is the foundational cause of the increasing prevalence of feminized men in society.
Now it's time to take a look at the cultural and social pressure on men to adopt a feminized mindset and societal presentation.
The Feminization of Public Education
This cultural programming has been occurring for at least as long a public education has existed.
Take at hazard one hundred children of several educated generations and one hundred uneducated children of the people and compare them in anything you please; in strength, in agility, in mind, in the ability to acquire knowledge, even in morality—and in all respects you are startled by the vast superiority on the side of the children of the uneducated.
— Count Leo Tolstoy, "Education and Children" (1862)
Beginning in the 1830s, the teaching profession completely transformed in its legitimacy, its expectations, and its demographic makeup. Specifically, these years saw teachers change from primarily untrained male farmers teaching as a secondary occupation, to highly qualified and educated people performing these jobs full time, most of whom were women.
The changes in the school system that caused the changes in the teaching profession are called the formalization of schools. The resulting effect to the teachers is called the professionalization or formalization of the teaching profession. The change in gender makeup of the teaching profession is referred to as the feminization of teaching.
The dramatic shift in gender makeup of teachers in the nineteenth century is one of the greatest changes in gender transformation of a single profession in recent history. While the timing, speed, and severity of the phenomenon was at times different from region to region and even from school to school, the overall trend seemed to be inevitable.
In St. Louis, Missouri, for instance, male and female teachers were employed equally in 1844. But as soon as 1858, female teachers outnumbered males by more than a 5:1 ratio. While the specifics may be different for factors that will be explored throughout this paper, the trend happened consistently in schools throughout the country. Towards the end of the nineteenth century, females completely dominated the teaching profession.
There are very few professions in the 19th century where men and women co-existed. For a brief period, teaching was one of these few professions. The formalized school system increased the length of the school year, which disallowed men from pursuing teaching as a secondary occupation to supplement their incomes as farmers, tradesmen, etc. Furthermore, the increased standards for teaching certification were an additional obstacle that women were willing to handle, and at the same time pushed men away. Finally, the average teacher salary was inadequate to support a family, a duty that was generally the responsibility of the patriarch in this era.
After the Civil War, utopian speculative analysis regarding isolation of children in custodial compounds where they could be subjected to deliberate molding routines, began to be discussed seriously by the Northeastern policy elites of business, government, and university life. These discussions were inspired by a growing realization that the productive potential of machinery driven by coal was limitless. Railroad development made possible by coal and startling new inventions like the telegraph, seemed suddenly to make village life and local dreams irrelevant. A new governing mind was emerging in harmony with the new reality.
The principal motivation for this revolution in family and community life might seem to be greed, but this surface appearance conceals philosophical visions approaching religious exaltation in intensity—that effective early indoctrination of all children would lead to an orderly scientific society, one controlled by the best people, now freed from the obsolete straitjacket of democratic traditions and historic American libertarian attitudes.
Forced schooling was the medicine to bring the whole continental population into conformity with these plans so that it might be regarded as a "human resource" and managed as a "workforce." No more Ben Franklins or Tom Edisons could be allowed; they set a bad example. One way to manage this was to see to it that individuals were prevented from taking up their working lives until an advanced age when the ardor of youth and its insufferable self-confidence had cooled.
In a speech he gave before businessmen prior to the First World War, Woodrow Wilson made this unabashed disclosure:
We want one class to have a liberal education. We want another class, a very much larger class of necessity, to forgo the privilege of a liberal education and fit themselves to perform specific difficult manual tasks.
By1917, the major administrative jobs in American schooling were under the control of a group referred to in the press of that day as "the Education Trust." The first meeting of this trust included representatives of Rockefeller, Carnegie, Harvard, Stanford, the University of Chicago, and the National Education Association. The chief end, wrote Benjamin Kidd, the British evolutionist, in 1918, was to "impose on the young the ideal of subordination."
At first, the primary target was the tradition of independent livelihoods in America. Unless Yankee entrepreneurialism could be extinquished, at least among the common population, the immense capital investments that mass production industry required for equipment weren’t conceivably justifiable. Students were to learn to think of themselves as employees competing for the favor of management. Not as Franklin or Edison had once regarded themselves, as self-determined, free agents.
Only by a massive psychological campaign could the menace of overproduction in America be contained. That’s what important men and academics called it. The ability of Americans to think as independent producers had to be curtailed. Certain writings of Alexander Inglis carry a hint of schooling’s role in this ultimately successful project to curb the tendency of little people to compete with big companies. From 1880 to 1930, overproduction became a controlling metaphor among the managerial classes, and this idea would have a profound influence on the development of mass schooling
In a section of Public Education called "A New Lengthening of the Period of Dependence," in which Ellwood P. Cubberley explains that "the coming of the factory system" has made extended childhood necessary by depriving children of the training and education that farm and village life once gave. With the breakdown of home and village industries, the passing of chores, and the extinction of the apprenticeship system by large-scale production with its extreme division of labor (and the "all conquering march of machinery"), an army of workers has arisen, said Cubberley, who know nothing.
Furthermore, modern industry needs such workers. Sentimentality could not be allowed to stand in the way of progress. According to Cubberley, with "much ridicule from the public press" the old book-subject curriculum was set aside, replaced by a change in purpose and "a new psychology of instruction which came to us from abroad." That last mysterious reference to a new psychology is to practices of dumbed-down schooling common to England, Germany, and France, the three major world coal-powers (other than the United States), each of which had already converted its common population into an industrial proletariat.
In 1933, an executive director of the National Education Association announced that his organization expected "to accomplish by education what dictators in Europe are seeking to do by compulsion and force." You can’t get much clearer than that. WWII drove the project underground, but hardly retarded its momentum. Following cessation of global hostilities, school became a major domestic battleground for the scientific rationalization of social affairs through compulsory indoctrination. Great private corporate foundations led the way.
Thirty-odd years later, between 1967 and 1974, teacher training in the United States was covertly revamped through coordinated efforts of a small number of private foundations, select universities, global corporations, think tanks, and government agencies, all coordinated through the U.S. Office of Education and through key state education departments like those in California, Texas, Michigan, Pennsylvania, and New York.
One of the documents to result from these efforts was the gigantic Behavioral Science Teacher Education Project, outlining teaching reforms to be forced on the country after 1967. The document sets out clearly the intentions of its creators—nothing less than "impersonal manipulation" through schooling of a future America in which "few will be able to maintain control over their opinions," an America in which "each individual receives at birth a multi-purpose identification number" which enables employers and other controllers to keep track of underlings and to expose them to direct or subliminal influence when necessary. Readers learned that "chemical experimentation" on minors would be normal procedure in this post-1967 world, a pointed foreshadowing of the massive Ritalin interventions which now accompany the practice of forced schooling.
The Behavioral Science Teacher Education Project identified the future as one "in which a small elite" will control all important matters, one where participatory democracy will largely disappear. Children are made to see, through school experiences, that their classmates are so cruel and irresponsible, so inadequate to the task of self-discipline, and so ignorant they need to be controlled and regulated for society’s good. Under such a logical regime, school terror can only be regarded as good advertising. It is sobering to think of mass schooling as a vast demonstration project of human inadequacy, but that is at least one of its functions.
Our form of compulsory schooling is an invention of the State of Massachusetts around 1850. It was resisted — sometimes with guns — by an estimated eighty percent of the Massachusetts population, the last outpost in Barnstable on Cape Cod not surrendering its children until the 1880s, when the area was seized by militia and children marched to school under guard.
― John Taylor Gatto, Dumbing Us Down: The Hidden Curriculum of Compulsory Schooling
The three main goals of early common schools: republicanism, Protestantism, and capitalism. Republicanism refers to the importance placed on virtue and discipline in early common schools. Similarly, Protestant ideas were taught through a curriculum heavily based on morality. The teaching of morality, not literacy or knowledge, was the main goal of these early common schools. Finally, capitalism was taught through the orderly nature of schools and the use of corporal punishment. Combined with the rigid structure of the school day, order and corporal punishment prepared students for their likely futures as factory workers.
Since the late 1800s, the mass production system that is public education, has been dominated at the classroom level by women teachers, with an almost total exclusion of men in the classroom.
Since the premise, behind which these boys and girls were mass produced, has been based on instilling lack of initiative, compliance and uniformity regardless of the sex of the child, it has been inevitable that the resulting product would be some sort of androgenous creature that would lean far more towards the feminine than the masculine, given that the vast majority of teachers serving as examples for role models, have been women. And this is on top of the fact that, for most children, their primary adult role model at home has also been a woman.
The Androgenous Industry and Economy
Prior to the Industrial Revolution, which occurred roughly between 1760 and 1840, the roles of men and women were closely aligned to their typical masculine and feminine tendencies, with men projecting their efforts outside the home and women concentrating their efforts within or near the home, while raising children. Initiative, inventiveness and daring was always an essential aspect of the male life, while continuity, safety and security was always an essential aspect of female life. The two different approaches to life served to balance each other out, creating a strong foundation for the continued existence of the human race.
The Industrial Revolution, through mechanization, began a long process of creating technologies that created an ever increasing androgenous work environment that has effectively eliminated the need for the gender specific livelihoods that existed since the beginning of civilization. The introduction of public education and other childcare programs, enabled women to move out of their home based focus and join men as part of the industrial workforce.
Once women focused more of their attention outside of the home, they also, understandably, began to demand more input and control of the wider society, socially, politically and economically. The right to vote was fought and won, followed by a growing women's movement to achieve total equality with men in all aspects of society.
Since the goal of the Financier/Oligarchs molding society, was to create a compliant androgenous work force, while also taking all control away from the family unit, vast amounts of resources were devoted to the women's movement to enable women to gain complete equality with men.
Out of this effort resulted the Women's Liberation Movement in the 1960s with notable leaders such as Betty Friedan (Betty Naomi Goldstein) and Gloria Steinem. What's with the name Naomi and feminism anyway?
Betty Friedan was one of the founders of the National Organization for Women (NOW) and a co-signer of the original (1966) Agenda of NOW.
According to Goldstein:
We do not accept the traditional assumption that a woman has to choose between marriage and motherhood, on the one hand, and serious participation in industry or the professions on the other.
And:
WE REJECT the current assumptions that a man must carry the sole burden of supporting himself, his wife, and family, and that a woman is automatically entitled to lifelong support by a man upon her marriage, or that marriage, home and family are primarily woman's world and responsibility-hers, to dominate-his to support.
This all sounds good at first glance, but regardless of what it sounds like, it is but one way by which to attempt to entice women, the majority of whom are found in poll after poll to prefer to be stay-at-home, married moms, to enter the work force. Why would anyone promote an idea that most women don't like? The answer to that question may be found in the fact that the goal to bring women into the work force is an ancient goal of communism and that Betty Friedan was well into her thirties a devout and active functionary of the Communist Party of the U.S.A.
Even a cursory examination of the goals of the creators of the Communist ideology makes it clear that a primary goal of communism was to break up the family, raise children through state institutions and force men and women to function as equal wage slaves of industry.
Already in the original Communist Manifesto produced by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels in 1848/49 it was made clear that no society could be successfully restructured unless all established cultural and moral traditions would be abolished – amongst the objectives of Marx and Engels was the liberation of women from the servitude to commerce and industry that 19th century feminists had fought so hard and successfully to achieve.
As per a review, by professor David Horowitz, of Friedan's book, The Feminine Mystique, published in Salon Magazine Jan. 1999:
...the author of that book establishes beyond doubt that the woman who has always presented herself as a typical suburban housewife until she began work on her groundbreaking book was in fact nothing of the kind. In fact, under her maiden name, Betty Goldstein, she was a political activist and professional propagandist for the Communist left for over a decade before the publication of "The Feminist Mystique" launched the modern women's movement."
The review by professor Horowitz states further:
Professor Horowitz documents that Friedan was from her college days, and until her mid-30s, a Stalinist Marxist, the political intimate of the leaders of America's Cold War fifth column and for a time even the lover of a young Communist physicist working on atomic bomb projects in Berkeley's radiation lab with J. Robert Oppenheimer.
Her famous description of America's suburban family household as "a comfortable concentration camp" in "The Feminine Mystique" therefore had more to do with her Marxist hatred for America than with any of her actual experience as a housewife or mother.
So, "how much of the communist ideology that was such large part of Betty Friedan's life and, indeed, formed her life, made it into the ideology of the oppressive feminism that now covers all aspects of our lives, of society and civilization and threatens to smother us all?"
It's important to understand that the Communist movement in Russia was financed by Rothchild banking interests in the West.
On his father's side, Marx came from a family of rabbis. His father was the first in the line to refuse that road and instead he became a rich lawyer. His father gave up Judaism, we are told, and became a Lutheran, although we must assume that was just a pose. He married a Jewish woman anyway, and although we are always told she was “semi-literate,” the more important fact is that she was connected to a family of very wealthy bankers and industrialists. This was the Philips family, which later started Philips electronics. Outside of the royals, the Philips were and still are the richest people in Belgium.
Wikitree makes it easy to see that Karl Marx's grandmother Nanette Barent-Cohen was the first cousin of Henriette Barent-Cohen, who married Nathan Mayer Rothschild. Wow. This indicates it wasn't just the Phillips and Pressburgs bankrolling the Communism project, it was the even deeper pockets of Rothschild.
The growing socialist movement—which was closely allied at that time to the Republican revolutions fomenting all over the world—was seen as a danger to the rich. Marx was trained and sent in to splinter and disorient this movement, which he did. Marx was sent in to control the opposition. At every juncture, Marx manages to create factions rather than alliances. He deftly prevents any real action by always turning the socialists against themselves. He keeps them arguing over philosophical fine-points rather than encouraging direct and immediate action.
What we're looking at here is the bankrolling and use of similar tactics in the West by the same financier/Oligarchs in order to create a androgenous working proletariat, with the added dose of fascist feminism to prevent men and women joining forces to organize against the wage slavery of a monolithic fascist economic cartel.
Divide and conquer' is a standard operating procedure used by every despot that has ever reigned over an unwilling populace. And once race and class have been utilized, dividing the sexes is the final solution. Utilizing agents to create discord between the sexes was much more difficult when men and women, in order to survive, were required to closely join forces. Once industrialization occurred, with its androgenous workforce, and the same financier/Oligarchs also gained total control of the mass media and mass education system, the use of agents to create discord, became highly advantageous.
Communist agents such as Betty Friedan (Goldstein) and Gloria Steinem were utilized and enabled to institute the feminist movement in order to rapidly move the agenda forward.
The Oligarchs modus operandi is to finance and promote disgruntled minorities in order to destabilize and undermine the world. Feminism is a prime example. It pretends to be about giving women equal opportunity in the workplace when in fact it is devoted to discouraging women from seeking fulfillment in motherhood while castigating men as being hyper-masculanized, brutish, violent, controlling, unevolved beings.
If these lesser creatures could just act more like women, then all would be good in the world.
It should be obvious by now that this feminist war against men is deliberate misdirection away from the source of the real fundamental systems of control that exist. Many millions of innocent women have been fooled into supporting this operation by the relentless onslaught of propaganda spewed by the controlled media and thru the controlled public education system. And countless numbers of boys and girls have been psychologically damaged by the agents that strategized and implemented this operation.
The best thing that should happen regarding both boys and girls is to get everyone off their backs. The government and media need to be taken out of their lives completely and they need to be re-integrated back into a functioning home. But those behind the big think tanks, like the American Enterprise Institute (AEI), don't want you to see that, because that would take a huge market away from the financiers/Oligarchs. AEI is a top fascist think-tank, in other words, promoting their various policies of middle-class ruination and financial depredation.
You can't nurture masculinity in any climate of hyper-socialization. The type of independence both girls and boys need isn't fostered by any government program, not on the federal level or even the local level. It isn't even “fostered” at home, strictly speaking. Independence isn't fostered, it is allowed. Obviously, the most independent child will be one left alone to a great extent to form his or her own opinions about the world. That child may then have something to add to society and civilization. A child “fostered” at every point and during every waking moment can only turn out to be a slave of some sort.
If there is resistance to the new feminine fascism, [going] back to the old masculine fascism, where men were completely formed by top-down control by other men, [will be no solution]. But this manufactured debate isn't even worth entering: we can't go back to the past in this one way, since the world isn't what it was in 1950, much less 1900. Unless the huge propaganda machine hovering over the heads of both boys and girls is disassembled, it won't matter if boys are quiet or talkative, competitive or cooperative, masculine or feminine. Neither boys nor girls will have a chance of physical or mental health in a world run by corporations and dominated by liars and psychopaths.
In the end, it doesn't matter if boys are squashed under a masculine or feminine fascism: either way they are squashed.
Pushing of a return to same-sex education is a similar disaster. Don't believe for a moment that separating the boys from the girls will help either of them. Nor should you believe the idea is being pushed to help boys.
Separating the sexes is just another way to traumatize them. It has been part of the long-term project to isolate the sexes. If men and women are separated from each other, mistrust each other, and are constantly bickering, not only can they not make alliances or successfully resist the governors, they cannot even gratify one another in the old ways. The financiers don't want males and females gratifying one another for free. That doesn't put money into anyone's pocket, does it? They want you purchasing porn and sex-toys and hookers and the various other sexual crutches of modern society. Those are billion-dollar industries—industries they now control. So of course they are going to push this return to same-sex classrooms.
The same-sex classrooms also help them promote homosexuality. In the old days, the same-sex classes weren't created to promote homosexuality: it just happened that way. Humans are adaptable creatures, and they learn to make do with what is available. But today the Plutocrats are promoting homosexuality, and it has to do with their plans for population control. It is a way to address overpopulation without passing Chinese one-baby laws and the like.
Homosexuality is also being promoted because the governors believe gays are less likely to resist them. The Plutocrats see most gays as they see women: more easy to control with emotional “arguments” and other societal misdirection. But since it would appear many of the Plutocrats are also gay, it is hard to understand their reasoning in this. They must believe there are two types of gays.
The financiers also want to raise the new boy as a gentleman to take the final fire out of him. He will be too polite to speak out and too concerned for his fingernails to fight back. Of course this is as the governors want it. They prefer to rule over the meek, so they sell meekness as the crowning virtue. The same thing is going on with this reintroduction of the “gentleman”. As with everything else now, it is sold as the opposite of what it is.
The US education system is broken, but it wasn't broken by feminists or progressive educators. Feminists and progressive educators have been just two tools in a much vaster project of societal ruination, and until we address that project and its authors, we will get nowhere on any given question of policy. The past two decades have given us clues galore about who those authors are and what they are really up to, and it is past time we stared the beast down.
In conclusion, we see that once again both sides have been manufactured to misdirect you away from the real projects and the real players. Curious isn't it, that neither those in the manosphere nor those in the femosphere ever let on that the CIA exists, much less that the financiers behind the CIA exist. You would think the feminists would attack the Plutocrats directly, since a majority of them are indeed men. But you never see this, do you? You never see them attacking the men that really are controlling them and limiting their freedoms and mentally and physically abusing them. Why? Because those men really are controlling them. In other words, those women are being paid to attack punks in the manosphere as “haters”, not to attack the billionaire fascist paying their salaries.
Gender Identity: Nature vs. Nurture?
Hormones
The Brain and Neurodegeneration- Part 1
Wiping Out America..... Study Shows Depopulation Agenda Moving Full Speed Ahead
Can These Household Chemicals Crush Your Son’s Masculinity?
Are Chemicals Feminizing and Emasculating Men?
Defeminization and Masculinization
The truth about girls and boys, toys and TV
Neural Masculization and Feminization
Estrogen in the adult male reproductive tract: A review
The Underground History of American Education
Betty Friedan and her Lies- Mike Parker
Reading the Signs today's lesson: Karl Marx
The Devil's Work: Feminism and the Elite Depopulation Agenda



















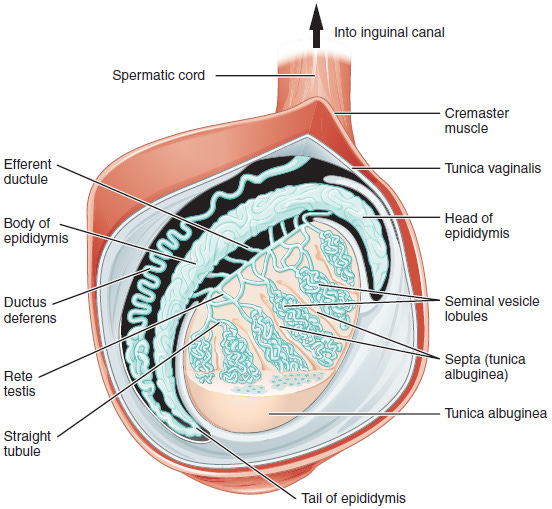

















































Wow!
A veritable tome is your research; the way you have built out each micro point while staying true and concise with the trajectory of the macro of the story is…great writing.
Thank you for doing this work.🥰